Health & Education
We all want the best care possible for our horses. The Heath & Education section covers both Learning Institutions, Organizations as well as many sources for equine assistance including Veterinarians and Farriers.
For those who want a to formally study horses, the Education section includes College Riding, Equine Studies, and Veterinary Schools. Learn about the wide variety of horses in the Horse Breeds section. Supplements and Treatments Therapy are also included in the section.
Everyone can learn from Fine Art and there are some specialty Museums that might surprise you.
Horses as a therapy partner enrich the lives of the disabled. These facilities are listed in our Therapeutic Riding section. To help children and young adults build confidence and grow emotionally, please see the resources available on the Youth Outreach page.
Looking for a place to keep your horse? You can find it in the Horse Boarding section. Traveling? Find a Shipping company or Horse Sitting service if your horse is staying home!
Want to stay up to date with the latest training clinics or professional conferences? Take a look at our Calendar of Events for Health & Education for the dates and locations of upcoming events.
Do we need to add more? Please use the useful feedback link and let us know!
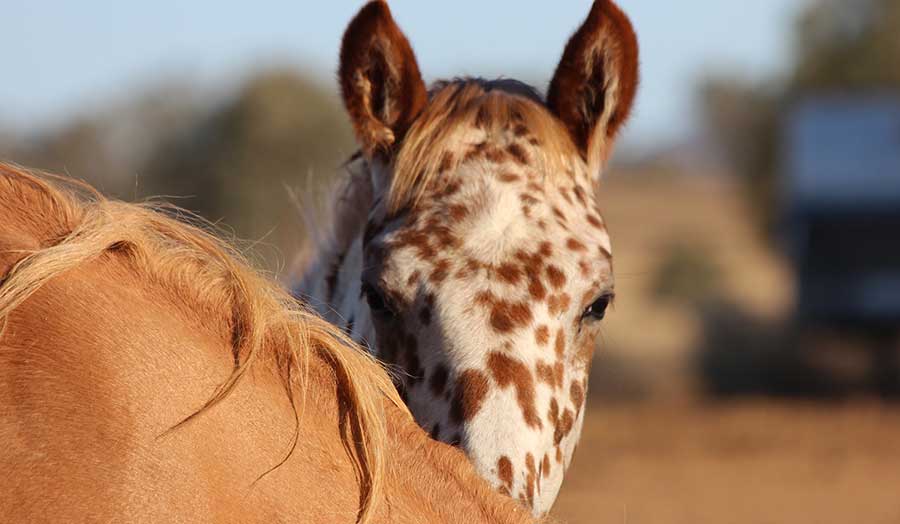

by Mary L. Scott
The breed goes back to the late seventeenth century, to the northwestern corner of North America and specifically to the large area that covered what is now part of the states of Oregon, Washington, Idaho, and Montana.
This was the land inhabited by the Nez Percé American Indians, and it is to their forward-thinking horsemanship and breeding practices that the Appaloosa owes its success.
Though the Nez Percé developed this spotted breed, the history of spotted horses is a long one, with images of spotted horses appearing in prehistoric European cave paintings from around 17,000 B.C.E.
Spotted horses-in particular the Austrian Noriker and the Danish Knabstrup - were extremely popular in Europe and were in great demand from the sixteenth century to perform in the increasingly popular Riding Schools. Many of the hallowed Spanish horses, too, including the revered Andalusian, once exhibited spotted coat colorings.
Read more: Appaloosa - The Most Beautiful Horse Breed in the World
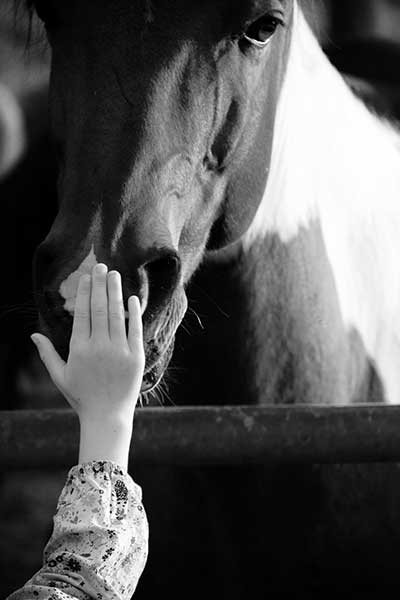

by Bob Burdekin
I would like to explain how we are continually moving forward into the area of working with horses that up to this time, has been completely ignored; and that area is emotional stress management in horses.
But before we can even discuss emotional stress management and how it affects your horse we need to look at how your horse's brain works and compare it to our own.
To start with horses do not think the same way that we do; their brain is structured in a totally different manner, and how your horse uses their brain along with your input becomes the causes of the various levels of stress that your horse may experience.
When we look at and compare the brain of the horse to that of our own, the most important area to consider is the area of the "frontal lobe".
In our brain the frontal lobe is extremely large and well-developed, for this is the part of our brain that allows us to be able to process all of the information that we receive daily and that adds to our personalities, as well as our ability to develop cognitively, or reasoning abilities.
The exact opposite is true for your horse when we compare the same area the frontal lobe of your horse's brain is much more undeveloped and therefore does not give them anything close to the ability to reason through a problem even close to the ability that you or I have.
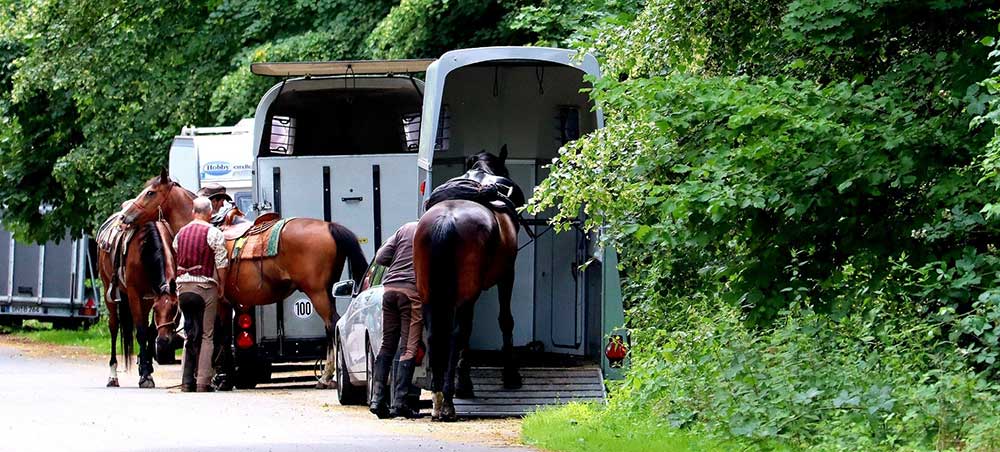

by Jennifer L Dayton
Horses walking into small, confined boxes on wheels can be a scary thing. Depending on previous experience, it can be either more or less scary. As a responsible horse owner, this is an important thing to teach your horse to do well, and to do it confidently and happily.
I believe all horses should learn this, although it is a much more significant part of the schooling of a competitive horse.
In general, whether the trailer is an angle-haul, straight-load, step-up, or ramp, a horse should follow pleasantly and comfortably behind the handler into any trailer. The horse should fit in the trailer, and not be hitting the ceiling or squished into the partitions.
To begin, most problems I have witnessed with loading have a lot to do with the horses' response to pressure on the halter. Body language is also important to recognize, as it is the horses' way of communicating with you. Some horses are terrified; some horses just say no, and have gotten away with saying no; and others have constant worries - not fitting properly, having had a bad experience, slipping or falling.
(A note to all those who drive a horse trailer: from those of us humans suffering from motion sickness - many of you make us feel ill with your quick turns and rapid accelerating and heavy braking; we have to wonder how many horses suffer the same way, and endure rough rides, knocking them about and challenging their balance constantly... not a good thing for horses to want to go back in the trailer for.
The most common problems encountered with trailering involve: the horse backing up, pulling back rapidly, refusing to move at all, dodging from side to side, or a combination thereof. Again, respect for the parts of the halter will help immensely.
If the handler applies pressure to the headstall of the halter, the horse should move forward. Pressure on the noseband should cause the horse to yield, and pressure on the sides of the halter should catch the side-to-side problems. The main pressure that needs to be responded to in loading is the headstall.
Read more: Horse Training Power Tip: Loading Difficult Horses Into Trailers

Electrolyte problems in the heat are directly proportional to sweat loss, so it makes perfect sense that horses working long periods are at greatest risk. This puts the spotlight on endurance horses.
Equine sweat is a concentrated electrolyte solution. Chloride is the most abundant electrolyte in sweat, followed by sodium, then potassium, with much smaller amounts of calcium and magnesium. The daily requirement for sodium can double with just one hour of low level sweating.
Even at low rates of sweating the horse will lose over a gallon of fluid per hour - and up to 4 gallons per hour with heavy sweating. That's a lot of fluid! The first consequence of this is dehydration. Since sodium lost in the sweat is needed to hold water in the body tissues, drinking water alone is not enough to correct the dehydration. Even mild dehydration has a major impact on the ability to perform.
Electrolyte losses triggered by exercise and sweating can produce a variety of temporary signs which respond to hydration and electrolyte replacement. Normal levels are required for regular heart rhythm, intestinal motility, coordinated movements of involuntary muscles like the diaphragm, skeletal muscle contraction and relaxation and the regulation of nerve firing.
Endurance horses show some typical changes in their blood electrolyte profiles. Low chloride is common. As above, chloride is very high in sweat. They do not have good stores of chloride in the tissues to replace what is lost in sweat. Low potassium is more common than low sodium. This is because horses can pull sodium from the tissues surrounding the body's cells to keep blood levels up. The kidney also conserves sodium by reducing sodium in the urine and replacing it with potassium.
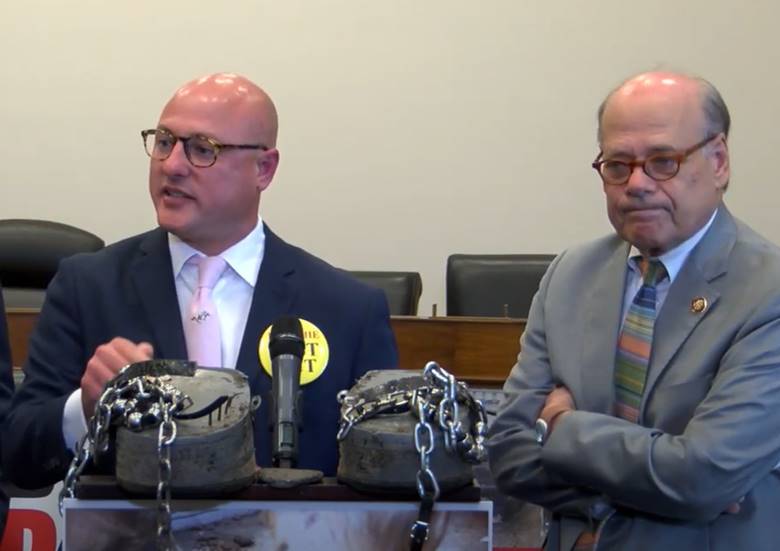

Animal Wellness Applauds Cohen’s Tireless Work for Horses.
WASHINGTON, D.C. July 2, 2020 – Today, the U.S. House of Representatives passed H.R. 1400, the Horse Transportation Safety Act, authored by Rep. Steve Cohen (D-TN-09), that would ban the transportation of horses across state lines in ‘double decker’ trucks or trailers containing two or more levels stacked on top of one another.
“I applaud Rep. Steve Cohen for his tireless work and dedication to horse protection -- he’s a knight in shining armor to the voiceless we care so deeply about,” said Marty Irby, executive director at Animal Wellness Action, and past president of the Tennessee Walking Horse Breeders’ & Exhibitors’ Association. “The horses that have transported millions of Americans for centuries, themselves deserve to be transported in a humane manner while they continue to bring joy, emotional support, and economic benefits to horsemen and women across the nation.”
“Horses deserve to be transported in as humane a manner as possible. Double-deck trailers do not provide adequate headroom for adult horses, and accidents involving double-deck trailers are a horrendous reminder that the practice is also dangerous to the driving public,” said Congressman Steve Cohen (D-TN-09). “I’m pleased this important measure is included in HR. 2, the Moving Forward Act.”
Double decker trucks and trailers present tremendous transportation risks to both the horses on board, and motorists sharing the state, federal, and local roadways with them. Numerous crashes that have occurred along interstate highways have resulted in not only the deaths of the horses, but innocent travelers as well. Even the U.S. Department of Agriculture has openly declared that these vehicles “do not provide adequate headroom for equines,” and that equines are far more likely to face injury in double decker trailers than in one level trailers that can better transport them.
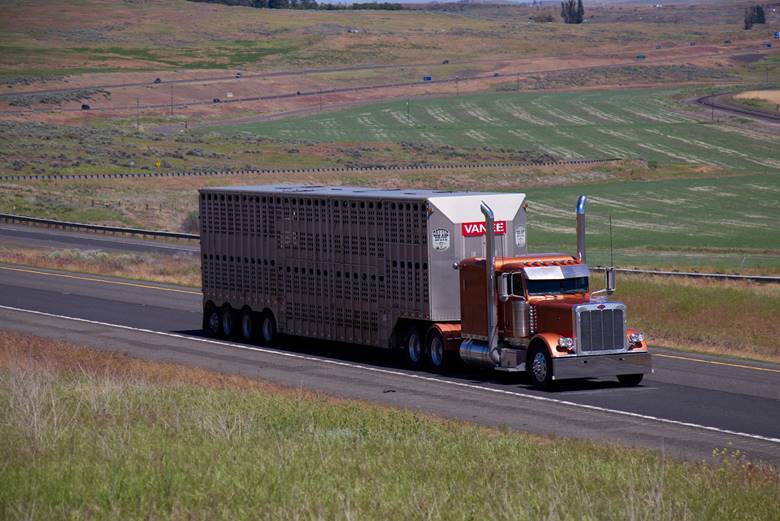

Read more: U.S. Rep. Steve Cohen Ushers Horse Transportation Safety Act to Passage

Today, more and more individuals are choosing to give an unwanted horse a second chance. Whether through purchase, adoption, or rescue, the horse in the “wrong” situation has a chance to find his way to the “right one.” Dr. Stacie Boswell’s goal is to restore health and comfort to every horse in transition, and to help him learn how to function as the horse he is expected to be. In her new book THE ULTIMATE GUIDE FOR HORSES IN NEED she has compiled hundreds of case studies highlighting the areas of concern in the rescue and details proactive methods of handling common medical problems and health issues, from nutrition and dentistry to deworming and hoofcare to traumatic injury and emergency rescue scenarios.
“Dr. Stacie Boswell has created a book that is packed with extremely valuable information for not only equine rescues, but a book that horse owners in general can also glean a lot from. She takes a pragmatic and all-inclusive approach to explaining the good, the bad, and the ugly involved when it comes to operating an equine rescue successfully. The Ultimate Guide for Horses in Need is a must-have book for both current rescues and those thinking of taking the leap into horse rescue—the importance of knowledge in this field cannot be underestimated if you want to run a truly successful rescue operation, and Dr. Boswell provides a solid foundation of that knowledge.” —Ashley Harkins, Director, United Horse Coalition
Read more: A Vet’s Guidance for Saving Horses in Need, Plus Training Your Eye to Nail the Distance

by Eleanor M. Kellon, VMD
Eating grass seems like the most natural thing in the world for a horse, but the grass in managed pastures bears little resemblance to what is available to a feral horse. The other part of the scenario that is very different, is that the feral horse will often travel an average of 20 miles a day — much more exercise than domesticated horses get.
Exercise is the best way to keep insulin and glucose in good control. Otherwise, tight restriction of sugar and starch intake to no more than 10% of the diet is needed.
Spring growths of grass at their peak almost invariably exceed that limit. They are extremely dangerous for any horse with problems in controlling insulin. Areas that experience considerable regrowth in the fall after high summer heat, may have a similar high sugar scenario at that time.

By Dr. Stacie Boswell
In order to prepare yourself and your horse for a possible disaster, the first step is to learn about your locale. Evaluate disasters your community has experienced in the past. Look at your terrain and determine what type of disaster is most likely. Consider where, specifically, your horse is housed. He could be at the base of a forest, near a river, or on the plains, rendering him susceptible to fire, flood, or tornadoes. If you live near railroad tracks or industry, hazmat exposure may be a real threat.
Find your local community emergency response team (CERT). Contact may be available through your local extension office. There is a CERT in every state. Learn what they recommend—they know local disasters best. Although many evacuation guidelines are general, it does you no good to prepare for a volcano if you live in Kansas. Training and credentialing workshops are available nationwide for individuals interested in learning to be a team member of a certified rescue effort.
Plan Ahead
The severity and number of weather-related disasters is on the rise. According to a Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) survey, fewer than 40 percent of people have an emergency plan. After careful consideration of the possible disasters that may strike in your area, organize yourself and prepare. Your horses are your responsibility, and good preparation will keep you ready in case you are displaced for any reason.
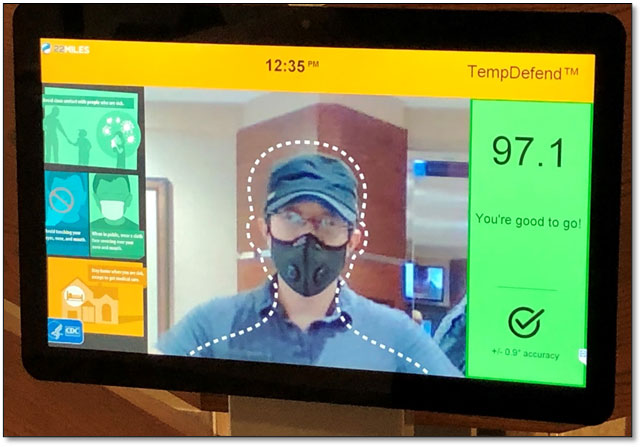
by CL Cimino
In 2020, seemingly without warning, the world changed. The COVID-19 virus seemed to attack everywhere, simultaneously. Businesses and lives were disrupted. Now we focus on getting back to work safely. We must figure out the next steps—how to open our business and how to stay in business if there is a second wave of COVID-19. And, how do we prepare for the future beyond COVID-19.
We are concerned first-and-foremost with the welfare and health of employees, participants, fans and customers - what are the initial steps a business should follow? Businesses are required to provide reasonable protections for their workers. Thermal Scanning is a critical component of demonstrating to your customers, local, state and government agencies that your business is taking reasonable protection measures.
March 17, 2020 the U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) issued an update to its guidance that now expressly acknowledges that employers may implement temperature screening measures in response to the current COVID-19 pandemic. The EEOC noted that “because the CDC (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention) and state and local health authorities have acknowledged community spread of COVID-19, and issued attendant precautions, employers may measure employees’ body temperature.”

Challenges for the Equine Business
No business is immune to the ravages of the virus: we must figure out what to do—how to stay in business—and how to protect ourselves and others while we wait for the long-awaited vaccination that hopefully will save millions of lives.
So, what can the equine industry do, to safeguard against the spread of the virus and assure our participants, fans and customers that horse business administrators are concerned first-and-foremost with their welfare and health?
Racetracks, polo grounds, veterinary clinics, horse shows, rodeos, boarding farms, horse sales pavilions—all have different roles within multi-billion-dollar international equine industry. The reality is that, diverse as may be their missions—they all have two things in common, the very foundations of their endeavors: horses, and the humans who love them. Those humans may be owners, trainers, farriers, grooms, hotwalkers, or fans. Whichever the role, the humans in horse businesses need to be protected from the virus.
- Why I Did the Mustang Makeover—and Why I’d Do It Again
- Improve the Horse’s Balance, Movement, and Self-Carriage with These Easy Tail Exercises
- Q&A: Managing Arthritis in Horses
- The Benefits of Riding to Music
- How to Feed a Severely Neglected Rescue Horse
- Josh Lyons with Lyons Legacy Partner With Horses in Need
- Equine Disaster Preparation and Response
- Colostrum -- An Exceptional Superfood!
- What the Heck is PEMF Anyway?
- Deworming Your Horse? Reference this Comprehensive Q&A
- Equine Enteric Coronavirus
- Is Your Horse Protected Against These Disease Risks?
- Equine-Facilitated Psychotherapy: Facing Trauma With a Horse by Their Sides
- University of Kentucky’s Department of Veterinary Science Responds to Nocardioform Placentitis
- Odd Couples
- Born to Stretch — Long and Low
- Don’t Be So Hard On Yourself; 10 Ways to Stay Positive About Showing
- 3 Tips for Horse Riding With Epilepsy (and Confidence)
- Physical Signs of Damage Caused by Ill-Fitting Saddles
- Conception Failure in Mares: Seven Causes

































